Understanding the Omicron Variant: Key Insights and Implications
Written on
Chapter 1: The Emergence of Omicron
Recently, scientists identified a new variant of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in South Africa, which has raised significant concerns globally. Reported to the World Health Organization on November 24th, this variant, designated as Omicron (B.1.1.529), follows the Greek alphabet naming convention and has prompted immediate attention from experts and authorities worldwide.
Countries are reacting swiftly, with Israel implementing a complete border closure, while others like the U.K. and the U.S. have restricted entry from South Africa, where the variant was first detected. With researchers expressing concerns that it may already be too late to curb its spread, the situation is evolving rapidly.
Understanding the context surrounding the discovery is crucial. Historically, viruses often exhibit wave-like patterns in their transmission, similar to those seen in previous pandemics, such as the Bubonic Plague.
Before Omicron's detection, South Africa had just begun to recover from a severe surge caused by the Delta variant. Analyzing the trends in daily new cases and fatalities reveals distinct peaks corresponding to various outbreaks.
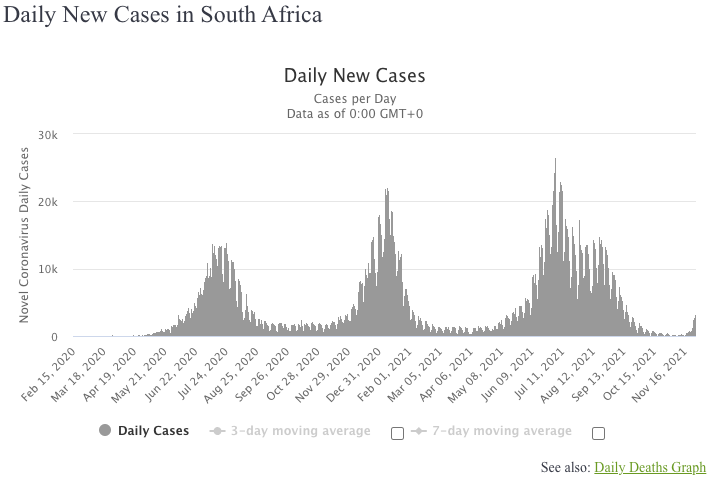
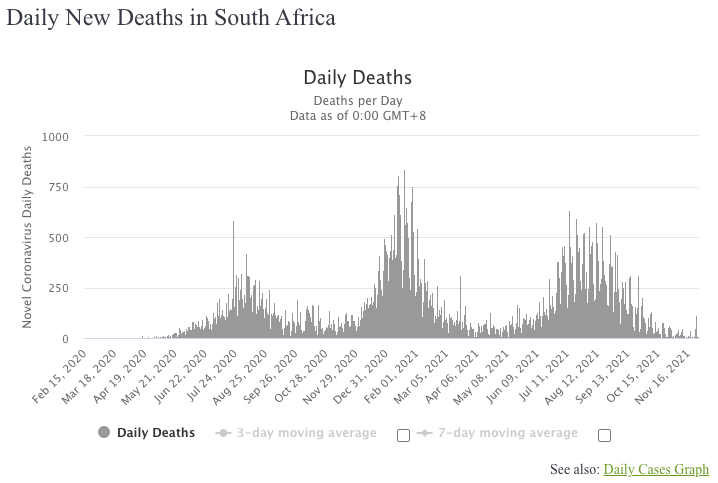
These fluctuations illustrate the recurrent nature of viral outbreaks, and as mutations occur, the virus tends to become more transmissible. The recent uptick associated with Omicron is particularly alarming due to its rapid increase in cases, suggesting a potentially significant impact on public health.
Section 1.1: Understanding the Speed of Spread
Typically, the pace at which infections rise is a reliable indicator of the outbreak's severity. This is why governments are acting quickly to close borders and mitigate spread—time is essential for preparation. In military terms, an unexpected rapid assault is the hardest to defend against before adequate measures are in place.
Currently, Omicron appears to be spreading faster than Delta, and the early cases have predominantly involved younger individuals. However, it's important to note the data is still limited, and drawing firm conclusions at this stage may be premature.
Subsection 1.1.1: Assessing Contagiousness and Severity
The preliminary data regarding Omicron’s transmissibility is troubling. Reports indicate that it has rapidly become the dominant strain in South Africa. The speed of its spread raises questions about whether it results from inherent transmissibility or specific superspreader events.
Experts are particularly concerned about Omicron’s extensive mutations, which may enhance its ability to spread. Key mutations, including E484K, N501Y, and D614G, have been identified on the spike protein, which is crucial for the virus's ability to infect host cells.
Understanding the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2 offers further insights into its implications and characteristics.
Section 1.2: Vaccine Efficacy Concerns
A significant concern surrounding Omicron is its potential to evade vaccine-induced immunity. Given that the spike protein is the target of most COVID-19 vaccines, the presence of over 30 mutations on this protein raises alarms among scientists.
These vaccines work by teaching the immune system to recognize the spike protein as a threat. However, with the emergence of mutations, the body may struggle to identify the altered spike proteins, leading to reduced effectiveness.
The situation is still evolving, and while there is no definitive evidence suggesting that vaccines will fail against Omicron, researchers urge caution. Continued observation and preparedness remain essential as we navigate this ongoing pandemic.
Chapter 2: Implications for the Future
The Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529) as a SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern highlights the critical need for ongoing research and monitoring.
In conclusion, while the emergence of the Omicron variant has sparked fears, it is vital to remain informed and take necessary precautions. As we await more comprehensive data, staying vigilant and adaptable will be crucial in addressing the challenges posed by this new variant.