Exploring the Possibility of Faster-Than-Light Travel
Written on
Chapter 1: The Quest for Warp Drive Technology
Are we nearing the realization of faster-than-light warp drives? Recent studies are examining the physics necessary to develop a viable warp drive technology. The iconic phrase, “To boldly go where no one has gone before,” from the beloved science fiction series 'Star Trek,' has fueled humanity's curiosity about exploring the cosmos. However, achieving such speeds is not as simple as it sounds.
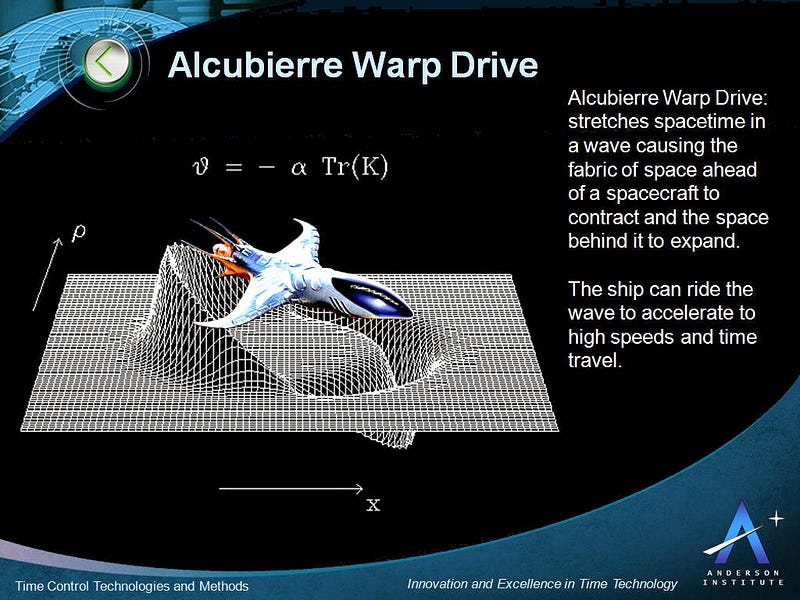
The concept of traveling at warp speeds—surpassing the speed of light—poses significant challenges. According to Einstein’s general theory of relativity, there exists a cosmic speed limit that prevents anything from reaching light speed. In 1994, Mexican physicist Miguel Alcubierre introduced a groundbreaking theory suggesting that it might be possible to warp space-time around an object, allowing it to travel faster than light.
The notion behind the 'Alcubierre Drive' is that a “wave bubble” would envelop the spacecraft, creating a zone of contracting space in front and expanding space behind. The spacecraft itself would not need to exceed light speed; instead, it would ride this wave, effectively achieving warp speed propulsion.
Despite this intriguing proposal, several significant obstacles remain:
- How can we generate a warp bubble?
- If a bubble is created, how do we extract the spaceship upon arrival?
- The most pressing issue is the immense amount of energy required to create such a bubble, estimated to equal the total mass-energy of Jupiter.
Section 1.1: The Role of Inspiration in Scientific Advancement
“I believe many share the sentiment that science fiction motivates the creation of technologies that can enhance our lives and open new avenues for discovery,” states Joseph Agnew, an undergraduate researcher at the University of Alabama, Huntsville. He is among the forefront of researchers exploring how to make warp drive technology a reality and recently presented his findings at the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) Propulsion and Energy Forum in Indianapolis.
Agnew noted that earlier estimates suggesting that creating a warp bubble would require all the energy in the universe have significantly decreased to the energy equivalent of Jupiter’s mass. Researchers are also investigating modifications to Alcubierre’s original design to further reduce energy requirements.
Advancements in quantum physics, quantum mechanics, and metamaterials may soon allow humanity to generate the energy necessary to create warp bubbles. This idea may not be as implausible as it once seemed. NASA is already investigating the potential creation of a warp bubble.
While we might be several decades away from achieving this technology, the rapid pace of technological innovation could transform this science fiction concept into a tangible possibility. If humanity aspires to explore deep space, warp drive technology will be essential, especially considering that the nearest major galaxy, Andromeda, is approximately 2.573 million light-years away.
The complete research can be found on the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics website.
Chapter 2: Scientific Perspectives on Warp Travel
The first video, "Faster-Than-Light Travel Is Possible, Physicists Say," discusses recent insights into warp drive theories and their feasibility.
The second video, "Can We Travel Faster Than Light? with Dr. Miguel Alcubierre," features a discussion with the original theorist behind the Alcubierre Drive, exploring the implications and challenges of this concept.