The Enigmatic Venus: A Planet of Contrasts and Challenges
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Venus
Venus, often dubbed as Earth's "sister" planet, has long captured the attention of astronomers. Its radiant brightness in the night sky once fueled hopes of discovering a beautiful world. However, exploratory probes have unveiled a reality starkly different from Earth—a hostile environment.
Why has enthusiasm for studying Venus waned? What hidden truths does this planet possess that evoke such a sense of despair? Additionally, what insights can it provide humanity regarding our own planet's future?

Chapter 2: The Extreme Conditions of Venus
Section 2.1: The Scorching Heat
Venus holds the title for the hottest planet in our solar system, with surface temperatures peaking at an astonishing 475 degrees Celsius, sufficient to melt metals like lead and tin. The intense heat is a result of its dense atmosphere, which is predominantly carbon dioxide, intensifying the greenhouse effect. Consequently, Venus's surface temperatures surpass those of Mercury, despite its proximity to the Sun.
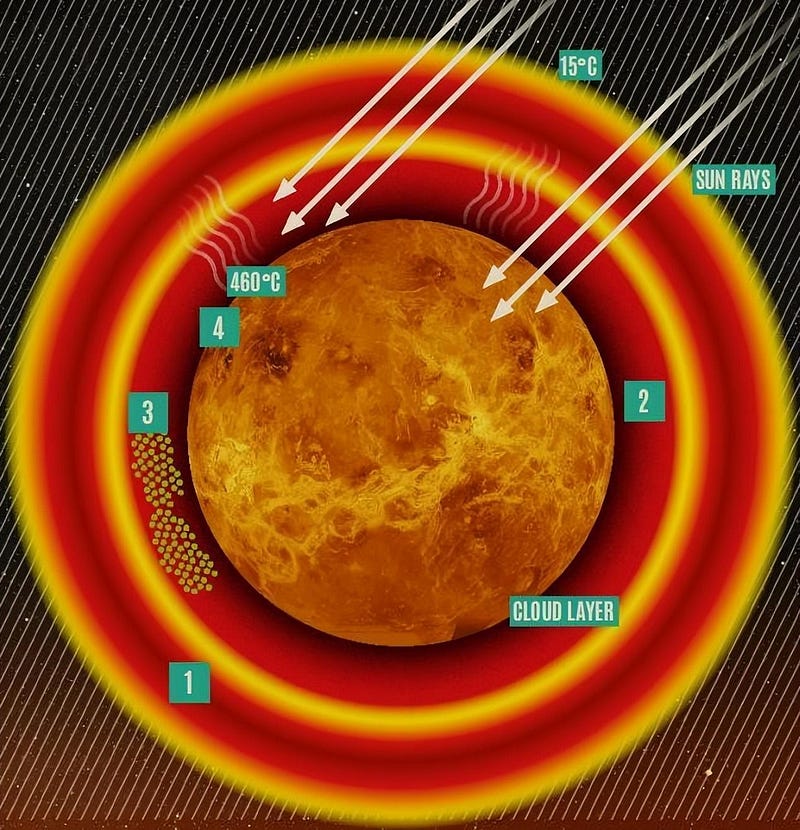
Moreover, the atmospheric pressure on Venus is a staggering 90 times that of Earth, making survival impossible for both humans and machines.
Section 2.2: Toxic Atmosphere and Violent Winds
The atmosphere of Venus is not only oppressive but also poisonous, filled with carbon dioxide and caustic substances such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and hydrofluoric acid. These corrosive materials damage equipment and machinery. Additionally, the planet experiences winds reaching 360 kilometers per hour, generating massive atmospheric vortices that rotate the cloud layers around the planet in just four days, while the planet itself rotates once every 243 days.

Venus's lack of a magnetic field, absence of liquid water, and stark indications of no life perplex scientists. The absence of a magnetic field could stem from its sluggish rotation or differences in its internal structure. The extreme conditions ultimately prevent any form of life from thriving.

Chapter 3: Diverging Evolutionary Paths
Section 3.1: A Tale of Two Planets
Despite their similarities in internal structure and distance from the Sun, Venus and Earth have taken radically different evolutionary routes. While Venus has transformed into a dry, lifeless planet, Earth has flourished with rich ecosystems and diverse life forms.

One theory suggests that an uncontrolled greenhouse effect on Venus led to skyrocketing temperatures, breaking down water molecules and resulting in a carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere.

The absence of Earth's plate tectonics, which help sequester carbon dioxide, alongside a lack of vegetation that can convert carbon dioxide into oxygen, could have contributed to this dire transformation.
Section 3.2: The Risks for Earth
The evolution of Venus serves as a stark warning for Earth’s future. It emphasizes the need for vigilance in protecting our planet from similar fate.

Chapter 4: The Mysteries of Venus
Section 4.1: Retrograde Rotation
Venus is unique in our solar system for its clockwise rotation, opposite to its orbit around the Sun. This peculiar rotation causes the Sun to rise in the west and set in the east.
With a day on Venus lasting 243 Earth days and a year only 225 Earth days, the temperature fluctuations between day and night can reach extremes, from scorching heat during the day to frigid cold at night.
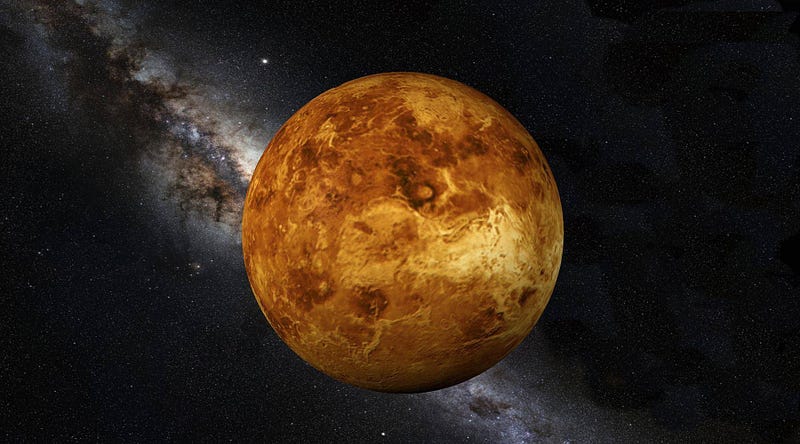

Section 4.2: The Phosphine Puzzle
The discovery of phosphine gas in Venus's atmosphere has sparked intrigue, as this compound is typically linked with microbial life on Earth. The presence of phosphine raises the question: could there be unknown life forms on Venus?
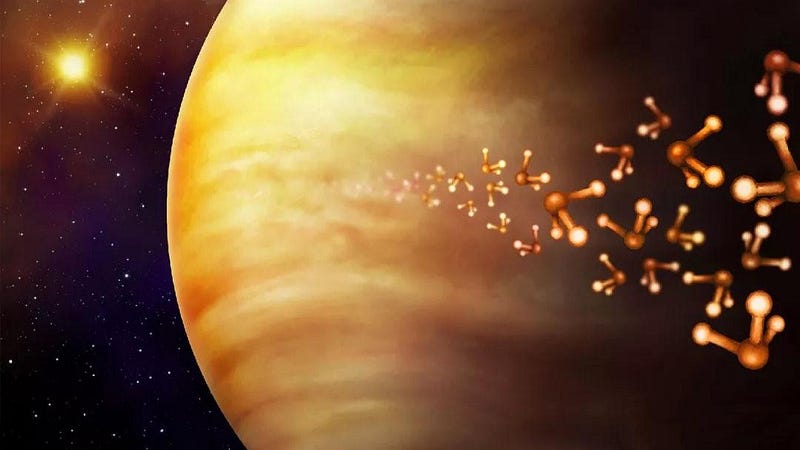
Despite extensive research, no definitive non-biological sources for phosphine have been identified, leading to speculation about its origins.
The first video, "Why Venus Didn't Turn Into Another Earth," explores the factors that led to the stark differences between Venus and Earth, shedding light on the evolutionary paths of these neighboring planets.
The second video, "Why NASA Won't Send Humans to Venus," discusses the challenges and dangers posed by the extreme conditions on Venus that deter human exploration.
Conclusion: The Future of Exploration
While the prospects for Venus appear bleak, we should approach the unknown with curiosity and determination. Continued exploration may yield crucial insights about Venus and the universe, expanding our understanding of the cosmos.