The Unseen Force: Solar Wind and Its Impact on the Solar System
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Solar Wind
Solar wind, a natural event emanating from the Sun's corona, can have significant and destructive effects if unprotected. For example, many people have witnessed the devastation caused by intense hurricanes on Earth, particularly Category 5 storms, which can exceed speeds of 157 mph (252 km/h) and obliterate infrastructure. In comparison, solar wind travels at an astonishing average speed of 0.87 million miles per hour (1.4 million km/h), far surpassing any terrestrial storm and extending to the heliosphere at the edge of our solar system.
The solar wind originates from the Sun's corona, the luminous halo visible during a solar eclipse. As it traverses space, this phenomenon creates stunning visual displays, such as the auroras on Earth. The interaction between solar wind and the Earth's magnetosphere produces the northern lights (aurora borealis) and southern lights (aurora australis), while also contributing to the green glows observed around Mars and Jupiter.
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, launched in 2018, is orbiting the Sun and gathering crucial information about solar wind. It aims to analyze the energy that heats the corona, accelerates the solar wind, and maps the structure of the wind's magnetic fields.
Despite the protective magnetic field our planet possesses, high-speed solar winds can create significant disturbances. Such storms can disrupt satellites, maritime communications, and power grids on Earth. Therefore, understanding solar wind's effects is crucial not only for life on Earth but also for future space explorations.
The first video, "How The Sun's Winds Shape Our Solar System," delves into the intricacies of solar wind and its influence across various celestial bodies.
Section 1.1: The Effects of Solar Wind
The consequences of solar wind extend beyond Earth. For instance, the massive planet Jupiter, with its robust magnetic field, effectively shields itself from most solar wind. Conversely, asteroids, lacking significant protection, are pounded by solar wind particles, which can alter their surface composition by ejecting material into space.
Subsection 1.1.1: Visualizing Solar Wind's Effects
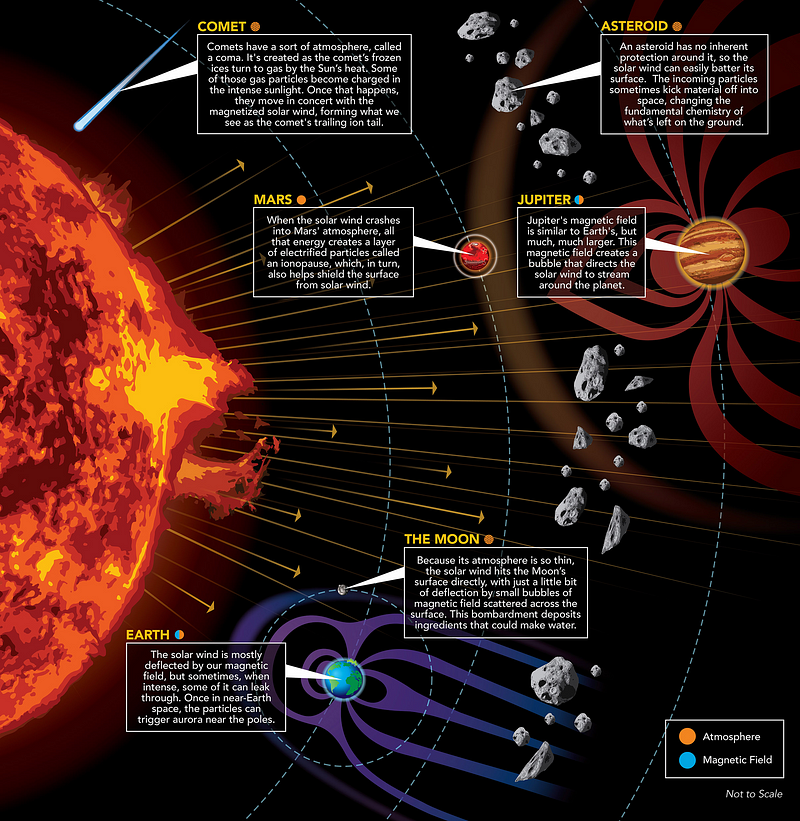
Chapter 2: The Future of Space Exploration
As we prepare for missions to the Moon and Mars, understanding solar wind becomes increasingly critical. These locations have thin atmospheres that offer minimal shielding against such cosmic forces.
The second video, "First 3D Map Of The Solar System Made Using Echoes Reveals the Heliosphere," explores how solar wind shapes the boundaries of our solar system and impacts space travel.