The Future of Wireless Connectivity: Transitioning from 5G to 6G
Written on
Chapter 1: The Evolution of Wireless Networks
The landscape of wireless connectivity is rapidly evolving as we transition from 5G to the anticipated 6G networks. This shift aims to create intelligent societies with a strong emphasis on automation.
5G represents the fifth generation of mobile wireless technology, boasting enhanced internet speeds, reduced latency, and improved reliability compared to its forerunner, 4G LTE. Over the years, we have witnessed regular updates to these networks as smartphones have become ubiquitous worldwide. Unlike previous generations such as 3G and 4G, 5G is regarded as a transformative leap rather than a mere enhancement.
One of the standout features of 5G is its remarkable speed, with theoretical maximums reaching up to 10 gigabits per second. This is a substantial upgrade from the theoretical cap of 300 Mbps for 4G LTE-Advanced, making 5G more than 30 times faster. Since its introduction in 2009, 4G LTE has dominated mobile technology, but the world is now transitioning to 5G, which was officially launched in 2019. This new standard has unlocked numerous possibilities, paving the way for innovations like autonomous vehicles, the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart cities. Looking ahead, the shift towards 6G is projected to occur by the decade’s end.
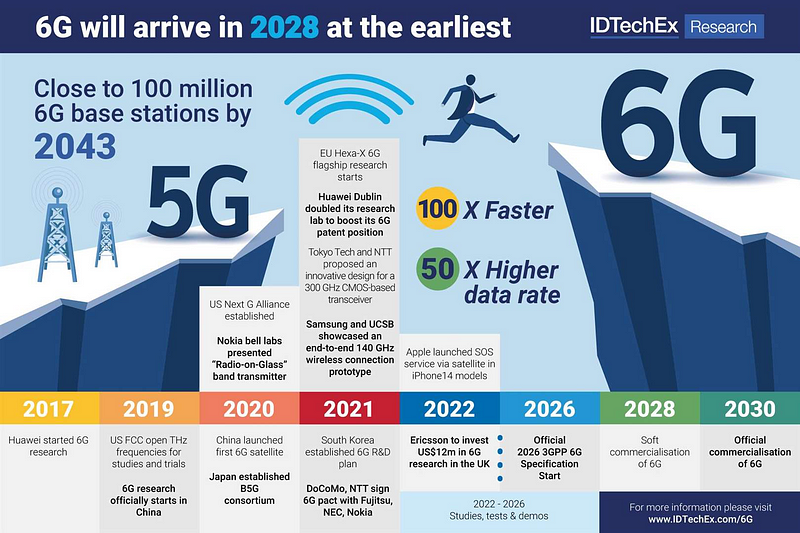
Chapter 2: Anticipated Advancements in 6G
As we set our sights on the horizon of wireless technology, the forthcoming 6G networks promise to deliver significant progress. A key enhancement of 6G over its predecessor is the utilization of higher frequency bands (ranging from 30 to 3000 GHz), which will facilitate faster data transfer and broader bandwidth. This will enable the handling of larger data volumes in shorter time frames, resulting in a smoother user experience.
The first video titled "5G NR transition Towards 6G: 6G Potential Technology and Innovation" delves into the transformative potential of moving to 6G, discussing the foundational changes this transition may bring.
One of the primary distinctions between 5G and 6G will likely revolve around speed and capacity. While 5G can achieve download speeds of up to 20 Gbps with latency as low as 1 millisecond—ideal for real-time applications like virtual and augmented reality—6G is expected to push these boundaries even further.
Some projections indicate that 6G could achieve speeds of up to 1 Tbps, marking a 50-fold increase over the current capabilities of 5G. Such advancements could enable groundbreaking applications, including remote surgeries and holographic communications. Additionally, 6G is anticipated to accommodate a vast number of devices, supporting up to 10 million devices per square kilometer compared to the 1 million limit of 5G.
The second video, "From 5G to 6G: The Key Challenges to Overcome | AI/ML IN 5G CHALLENGE," explores the obstacles that must be navigated in this transition and how AI and machine learning can play a role in overcoming them.
Energy efficiency is another critical difference expected between 5G and 6G. Currently, 5G networks consume substantial energy, a demand likely to rise as more devices join the network and data processing increases. Conversely, 6G aims for enhanced energy efficiency through innovative materials like graphene, which may allow for signal transmission with reduced energy requirements. Furthermore, researchers are investigating the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize network performance and minimize energy use.
Security and privacy are becoming paramount as the number of connected devices grows. 5G networks employ features such as network slicing and end-to-end encryption to safeguard against cyber threats. In contrast, 6G is projected to incorporate cutting-edge security measures, including quantum encryption, which leverages quantum mechanics to secure data transmission from interception. Although still in the nascent stages, this technology could significantly transform our approach to data security.
In conclusion, the potential of 6G extends beyond merely achieving faster speeds and increased bandwidth. It aims to tackle significant societal challenges by fostering reliable systems, enhancing sustainability through mobile technology, and expediting automation to enrich people’s lives—ultimately facilitating limitless connectivity for future communication needs. The promise of 6G signifies a future where technology plays an even more pivotal role in human advancement.